Anatomography
Anatomography is an interactive website which supports generating anatomical diagrams and animations of the human body. The Anatomography website is maintained by the DBCLS (Database Center for Life Science) non-profit research institute located at the University of Tokyo. Anatomical diagrams generated by Anatomography, and 3D polygon data used on the website (called BodyParts3D), are freely available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license.[1]
- Description
Anatomography was launched on Feb. 9, 2009 by founder and chief director Kousaku Okubo, professor of the DNA Data Bank of Japan at the National Institute of Genetics.
Human body polygon data used in the site is called "BodyParts3D". BodyParts3D polygon data is extracted from full-body MRI images. The MRI image set which BodyParts3D is based on is "TARO". Taro is a common given name for males in Japanese, as John is in English. TARO is a 2mm * 2mm * 2mm voxel dataset of the human male created by the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology. TARO was published freely on November, 2004.
The construction process of BodyParts3D is as follows.
- Phase 1: Additional anatomical segmentations were introduced in the original TARO data.
- Phase 2: Then, missing details were supplemented and blurred contours were clarified using a 3D editing program by referring to textbooks, atlases, and mock-up models by medical illustrators.
- Phase 3: Further segmentation and data modification will continue in collaboration with clinical researchers until sufficient concept coverage is achieved.
BodyParts3D polygon data is distributed in the OBJ file format. The entire data file's size is 127 MB (polygon reduced) and 521 MB (high quality) as of version 3.0.The number of body parts (organs) registered in BodyParts3D is 1,523 as of version 3.0.
License
Images generated by Anatomography and the polygon data included in BodyParts3D are licensed under the Creative Commons license, in hope of widening usage and democratizing medical knowledge.
Funding
The BodyParts3D/Anatomography project was funded by MEXT (Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology) from FY2007 to FY2010. As of FY2011, the project has been funded by the JST (Japan Science and Technology Agency).
Reception
Diagrams from Anatomography are used, for example, in Canadian science TV show Le code Chastenay, Internet encyclopedia Wikipedia, as lecture material in universities, and elsewhere to share knowledge.About usage of Anatomography on websites like Wikipedia and Wikimedia Commons, developers say "spreading of usages by anonymous users on like Wikipedia and Wikimedia Commons is what we had expected."
Technical features
BodyParts3D/Anatomography project uses the Foundational Model of Anatomy (FMA). The FMA is an open-source anatomical ontology developed and maintained by the Structural Informatics Group at the University of Washington. In BodyParts3D, each body-part is managed by an FMA identifier (FMAID) defined by the FMA. For example, the vertebral column is registered as FMA13478, the temporal lobe is registered as FMA61825, and so on.
Version history
- Version 1.0 (Feb. 9, 2009)
- Version 2.0 (Apr. 28, 2010)Total number of body parts is 1,324.
- Version 3.0 (Jun. 20, 2011) Total number of body parts is 1,523.
Similar services
- Zygote Body - Free web service provided by the Zygote Media Group located in American Fork, Utah, US. Zygote Body was launched as Google Body on December 15, 2010. The polygon data used on the website is a commercial product. As of October, 2012, the price of its full-body polygon data is $13,995.
- BioDigital Human - Free web service and commercial product provided by BioDigital, Inc. located in New York, New York, US. The BioDigital Human was published in 2011. The web site won a SXSW Interactive Award in 2013.
Others
A few tutorial videos on using Anatomography are available on YouTube, see external links.
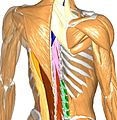
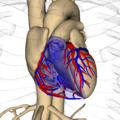
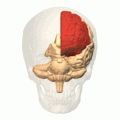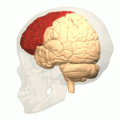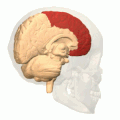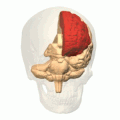
Additional images
See also
- Human anatomy
- Open science
- Open data
- Science Commons
- Democratization of knowledge
















No comments:
Post a Comment